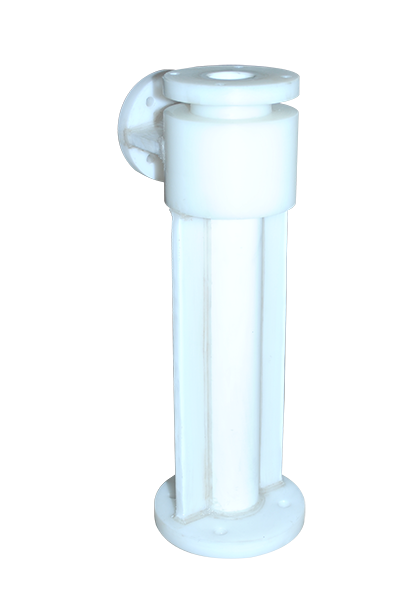
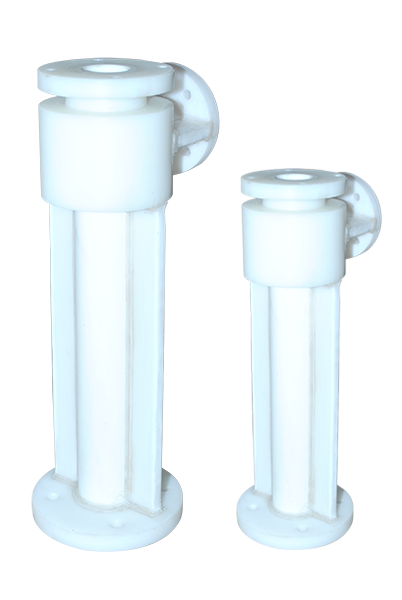
Vacuum Ejector |
We are renowned entity in the domestic as well as international market for proffering matchless range of the vacuum ejector, is developed meticulously in order to efficiently enacting respective operation. This vacuum ejector works as per the venturi principle, and extensively used to convert the pressure energy into velocity energy. The offered vacuum ejector has proven its potential in variegated industries by producing the considerable velocity energy in a short period of time without any interruption and for the same is commended by the end users. This vacuum ejector is available in the enormous specifications to match your needs at the farthest. |
 |
Principal of Jet vac units
High pressure motivating fluid is converted to high velocity. High velocity fluid entrains and transfers part of its momentum to the induced fluid. These mixed fluids at low velocity enter the diffuser, which is so shaped that it gradually converts's the velocity energy to pressure energy and discharges them to a pressure higher than suction pressure but lower than initial motivating fluid pressure.
|
|
| |
| Salient Features |
Matertial Of Construction |
- Absolute reliability.
- Robust and long working life.
- Can be made from many corrosion resistance material.
- Easy handling even of large suction quantities.
- low capital, installation and maintenance costs.
- Compact and light weight.
- No moving part to wear or to go out of order.
- Simple in operation.
- No sealing and lubricating liquids are required as in mechanical system as per eg:
Water ring vacuum pumps & high vacuum pumps.
|
Cast iron
| Cast Steel |
Carbon |
| Stainless Steel |
Lead |
| Monel |
Rubber Lined |
| Porcelain |
PVC |
| Teflon |
Poly propylene |
|
|
 |
|
| |
| Applications |
| Producing and maintaining high vacuum to moderate vacuum down to atmosphere in the following processes : |
| 1. Distillation |
| 2. Evaporation |
| 3. Refrigeration |
| 4. Crystallization |
| 5. Deodorisation |
| 6. Deaeration |
| 7. Drying |
| 8. Cooling (Evaporative) |
|
| 9. Vacuum Mettallurgy |
| 10. Filteration |
| 11. Degassing |
| 12. Debusting (in size reduction) |
13. Heating, Pumping, Mixing and Stirring of Fluids, induced fluids can be Gases, Liquids, Slurries or liquids with granular solids in suspensions. |
| 14. Exhausting and scrubbing of gases with liquids. |
|
|
| |
|
| |
| These Units Are Made in Following Types |
Sr. No.
|
Type
|
Range of Suction Pressure |
 |
1. |
Water Ejector |
32 mm. at shut off with 30°C water . |
2. |
One Stage Steam + Water Ejector |
10 mm Hg. abs. |
3. |
Two Stage Steam + One Stage of Water Ejector |
2 mm Hg. abs. |
|
|
| |
| Capacity Of Standard Units in M3/HR Free Air Displacement |
Hp |
1 |
2 |
3 |
5 |
7.5 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
M3/HR |
6.5 |
25 |
50 |
80 |
160 |
240 |
330 |
440 |
CFM |
4 |
15 |
30 |
50 |
95 |
140 |
200 |
260 |
Make Up Water LPM |
4 |
5 |
6 |
8 |
16 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
|
| |
| |